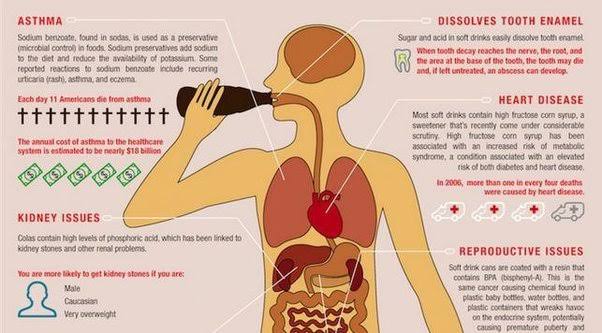
The Dangers of Soft Drinks: Why You Should Think Twice Before Drinking Them
Soft drinks have become a staple in modern diets worldwide, with millions of people consuming them daily. However, the sweetness and convenience of these beverages come with numerous health risks that make them one of the most dangerous items in our diets. From high sugar content to artificial additives, soft drinks pose significant dangers to our bodies and overall health. Here, we’ll explore the negative effects of soft drinks and why reducing or avoiding them is essential for a healthier life.
- High Sugar Content and Weight Gain
One of the most critical concerns about soft drinks is their high sugar content. A single can of soda typically contains about 10 teaspoons of sugar, which is already over the daily recommended limit for adults. Consuming such large amounts of sugar leads to several negative outcomes:
Increased Caloric Intake: Soft drinks provide “empty calories,” meaning they offer calories without any essential nutrients. This results in a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, followed by a crash that leaves you feeling hungry again, leading to overeating.
Weight Gain: Regular consumption of sugary beverages is directly linked to weight gain. Since liquid calories are not as satisfying as solid foods, people tend to consume more without realizing it. Over time, this caloric surplus leads to weight gain and obesity.
Insulin Resistance: Consuming high amounts of sugar frequently can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This condition is a precursor to diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
- Impact on Heart Health

Soft drinks are a known contributor to heart disease, particularly due to their effects on cholesterol and blood pressure levels. Here’s how they harm cardiovascular health:
Raised Blood Pressure: High sugar intake has been shown to increase blood pressure. For those who consume soft drinks regularly, this can create long-term risks of hypertension, which is a major risk factor for heart disease.
Increased Risk of Heart Attacks: Studies have found that people who consume sugary drinks daily are at a higher risk of heart attacks. The excessive sugars and artificial ingredients in soft drinks can raise “bad” LDL cholesterol and lower “good” HDL cholesterol, leading to heart issues over time.
- Negative Impact on Bone Health
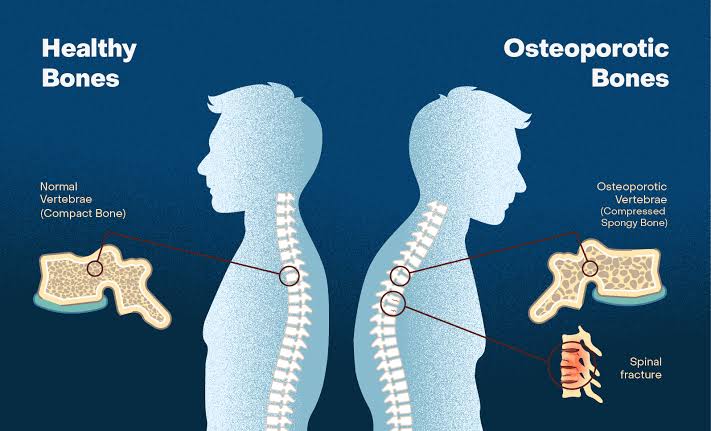
Soft drinks, especially those that are carbonated, have a negative impact on bone health. Phosphoric acid, a common ingredient in many sodas, can lead to the following issues:
Reduced Calcium Levels: Phosphoric acid affects the body’s ability to absorb calcium, a crucial mineral for bone health. As a result, regular soda drinkers may experience weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Increased Risk of Osteoporosis: Since calcium is leached from bones to balance the acidity caused by soft drinks, individuals who consume them frequently may be at a higher risk of osteoporosis, especially women, who are already more susceptible to this condition.
- Tooth Decay and Oral Health Problems
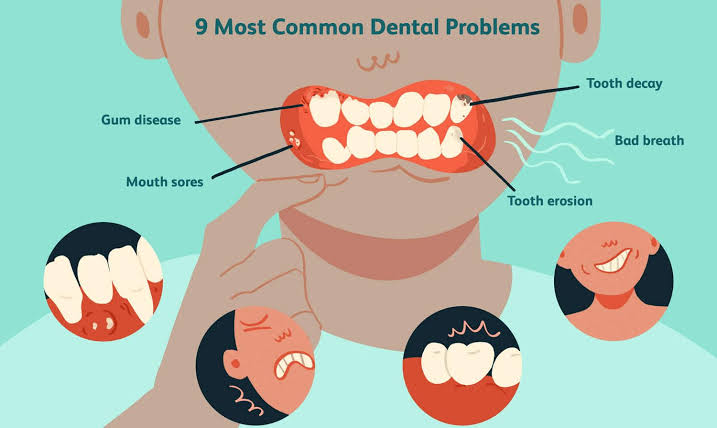
Soft drinks are notorious for damaging teeth due to their high sugar and acid content. Here’s how they harm oral health:
Tooth Erosion: The acids in soft drinks, such as citric and phosphoric acid, weaken tooth enamel, making it more susceptible to decay. Once enamel is eroded, it doesn’t regenerate, leading to lifelong dental issues.
Cavities: The high sugar content feeds bacteria in the mouth, producing acid as a by-product. This acid further damages tooth enamel, leading to cavities. Over time, people who consume sodas regularly may face severe dental issues that require expensive treatments.
- Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Soft drinks are a significant risk factor for developing Type 2 diabetes. Here’s how they contribute to the development of this condition:
Insulin Spikes: The high sugar content in soft drinks leads to quick spikes in blood sugar. Over time, the body struggles to keep up with these spikes, eventually leading to insulin resistance.
Increased Fat Storage: When blood sugar levels are high, the body stores excess sugar as fat. This process, especially around the abdomen, is linked to insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes.
- Harmful Effects of Artificial Sweeteners
Many people turn to diet sodas thinking they’re healthier, but artificially sweetened soft drinks come with their own risks. Here’s why they aren’t a safe alternative:
Potential Weight Gain: Artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin can alter gut bacteria, potentially leading to weight gain instead of weight loss. Some studies suggest that these sweeteners confuse the body, leading to an increased craving for sweets.
Link to Metabolic Disorders: There is evidence that artificial sweeteners may increase the risk of metabolic syndrome, a condition that includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and high cholesterol, all of which are risk factors for diabetes and heart disease.
- Mental Health Implications
The effects of soft drinks aren’t just physical; they can impact mental health as well:
Anxiety and Mood Swings: The caffeine and sugar in sodas can create a “sugar high” that may lead to temporary increases in energy. However, once the effects wear off, they can lead to mood swings, irritability, and anxiety.
Increased Risk of Depression: Some studies have linked the consumption of sugary beverages with an increased risk of depression. Regular intake of sodas, particularly those with artificial sweeteners, has been associated with a higher risk of depression over time.
- Liver Damage and Increased Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Soft drinks are high in fructose, a type of sugar that is processed in the liver. Unlike glucose, which can be used by cells throughout the body, fructose is mostly metabolized by the liver, leading to unique risks:
Fat Accumulation in the Liver: Excessive consumption of fructose leads to fat buildup in the liver, which can result in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD is an increasingly common condition that can lead to liver damage, inflammation, and even cirrhosis.
Increased Risk of Liver Disease: Regular consumption of sugary soft drinks is associated with higher rates of liver disease, even among individuals who do not consume alcohol.
- Effects on Kidneys
Drinking soft drinks also has implications for kidney health, as they contain phosphoric acid, caffeine, and high amounts of sugar:
Kidney Stones: The phosphoric acid in sodas has been linked to an increased risk of kidney stones. Regular soda consumption can create an imbalance in the body’s minerals, leading to painful kidney stones.
Reduced Kidney Function: Studies have shown that regular soft drink consumption is linked to reduced kidney function over time. This is particularly true for people who consume both sugary and artificially sweetened soft drinks.
Conclusion
Soft drinks are a widely consumed but highly dangerous part of many people’s diets. Their high sugar content, artificial additives, and acidic nature lead to a range of health issues, from obesity and diabetes to tooth decay and liver damage. While it may be challenging to cut out soft drinks entirely, the benefits of doing so far outweigh the temporary enjoyment they provide. Choosing healthier alternatives, such as water, herbal teas, or natural fruit juices in moderation, can lead to significant improvements in both physical and mental health. Reducing or eliminating soft drinks from your diet is a step toward a healthier and more balanced lifestyle, helping you to avoid the myriad health risks associated with these sugary, chemical-laden beverages.